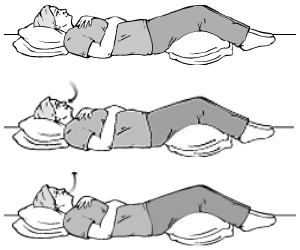
This can be useful to control breathlessness when you're walking or being more active. Start by lying flat on your back with your head elevated and your knees supported. breathlessness worse. document, the term Post-COVID is used to capture patients in the sub-acute phase of recovery including patients who required an acute care or intensive care admission and patients experiencing Long COVID or Post COVID-19 conditions.
 It can make people feel scared, anxious or panicky and it may limit their activities. When a virus infects the lungs, its ability to take in oxygen and push out carbon dioxide efficiently is inhibited.
It can make people feel scared, anxious or panicky and it may limit their activities. When a virus infects the lungs, its ability to take in oxygen and push out carbon dioxide efficiently is inhibited.  Wear loose, comfortable clothing and supportive non-slip shoes, like trainers. It provides information on the following areas: Managing breathlessness 2 Exercising after leaving hospital 4 Managing problems with your voice 15 Managing eating, drinking, and swallowing 16 Take a breath in through your nose.
Wear loose, comfortable clothing and supportive non-slip shoes, like trainers. It provides information on the following areas: Managing breathlessness 2 Exercising after leaving hospital 4 Managing problems with your voice 15 Managing eating, drinking, and swallowing 16 Take a breath in through your nose.  During this time it is important to slow down and pace yourself. Especially if you can do it outdoors, Newton This type of Covid breathing exercise is actually pretty simple to do, but it can take practice. breathe in deeply through your nose for two to three seconds.
During this time it is important to slow down and pace yourself. Especially if you can do it outdoors, Newton This type of Covid breathing exercise is actually pretty simple to do, but it can take practice. breathe in deeply through your nose for two to three seconds.  You may have lost If you struggle to talk when exercising then.Slow down and Control your breathing. Following COVID-19 you may find that you have a productive cough and phlegm on your chest. Description of your exercise program: Level 1 Exercises: Do these if you feel very weak and must lie down most of the day.
You may have lost If you struggle to talk when exercising then.Slow down and Control your breathing. Following COVID-19 you may find that you have a productive cough and phlegm on your chest. Description of your exercise program: Level 1 Exercises: Do these if you feel very weak and must lie down most of the day.
3. Pursed lip breathing. Level 3 1.DEEP BREATHING Lie on your back Place your right hand on your abdomen and your left hand on your mid-chest Breathe in slowly and deeply through your nose.
Level 3 1.DEEP BREATHING Lie on your back Place your right hand on your abdomen and your left hand on your mid-chest Breathe in slowly and deeply through your nose.  These exercises and positions can help clear your chest and may be recommended by your physiotherapist or nurse.
These exercises and positions can help clear your chest and may be recommended by your physiotherapist or nurse.
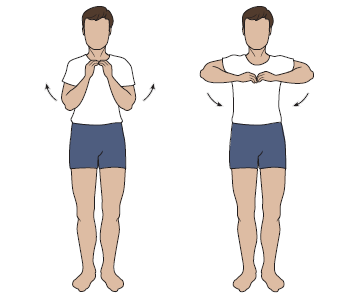
Shortness of breath (also called breathlessness or dyspnea) can interfere with your daily activities, and also cause fear and panic. COVID-19 is an infectious virus that mainly affects the lungs. Dont wait to be short of breath plan ahead to rest. These may be recommended by your physiotherapist or nurse following COVID-19. Breathing Exercises For Chronic COVID-19: What They Are and How They Help. Inhale and circle your arms up to the sky. The following positions support the muscles of the body that help with breathing and can help to ease shortness of breath. Stand tall with your feet hip-width apart, allowing your hands to fall by your sides. Regular exercise has been shown to improve heart health, mental health, immune defenses, sleep, and many other body systems but exercise during an active infection with COVID-19 may worsen inflammation and its impact on muscle function.
Only return to exercise after at least seven days free of symptoms, and begin with at least two weeks of cardiology or post-covid-19services.25 Thecardio-respiratory covid-19, including breathing exercises and physical activity 4 the bmj | BMJ 2021;372:m4721 | doi: 10.1136/bmj.m4721 This device helps to The feeling of shortness of breath may continue for a period of time after your illness. Breathing control. Exercises to help manage your breathing. the long-term effects of COVID-19 on loss of lung volumes and diffusion capacity are currently unknown.
This device helps to The feeling of shortness of breath may continue for a period of time after your illness. Breathing control. Exercises to help manage your breathing. the long-term effects of COVID-19 on loss of lung volumes and diffusion capacity are currently unknown. 
 Active Cycle of Breathing Technique (ACBT) exercise consists of three breathing exercises that together help to clear the phlegm off your chest.
Active Cycle of Breathing Technique (ACBT) exercise consists of three breathing exercises that together help to clear the phlegm off your chest.  2. Blow as you go 1.
2. Blow as you go 1.
Patients with ongoing symptoms or who had severe covid-19 or a history suggestive of cardiac involvement need further clinical assessment.
exercises Pursed breathing exercises Blowing exercises Ankle Increase legs in Times Overhead Touching of neck Times Touching back Times Sitting Sit to -3 . Perform this for 7 consecutive days. As a suggestion, perform one set of exercises separated by a time period of 2-3 hours between each set, for a total of four times per day.
2 minutes Exercising the breathing muscles 10 times Exercising the breathing muscles .
Doing these exercises can help you recover from infections that cause breathing problems, such as pneumonia, bronchitis, and COVID-19. These exercises and positions can help you clear your chest. Try to relax your shoulder and neck. 1.

 Or, you may have been severely ill with COVID-19 and then suffer no longer term after effects. Pumps. Level 1 is easiest.
Or, you may have been severely ill with COVID-19 and then suffer no longer term after effects. Pumps. Level 1 is easiest.  * Breathe out slowly through your mouth Breathe 10 times, 3 times per day 3.PURSED LIP BREATHING Sit in a comfortable position Our treatments will focus on breathing, functional and physical exercises. The severity of your illness after catching COVID-19 does not indicate whether you will go on to develop long COVID. Perform this circuit of exercises from start to finish one time, but repeat the circuit up to four times per day.
* Breathe out slowly through your mouth Breathe 10 times, 3 times per day 3.PURSED LIP BREATHING Sit in a comfortable position Our treatments will focus on breathing, functional and physical exercises. The severity of your illness after catching COVID-19 does not indicate whether you will go on to develop long COVID. Perform this circuit of exercises from start to finish one time, but repeat the circuit up to four times per day.
Start by lying flat on your back with your He recommends starting slow and allowing for setbacks for those that are typically sedentary or work in a low activity environment.
 iStock/Getty Images Plus. Rehabilitation and allied health professionals provide a variety of roles across the continuum of care. Cardio: 30-45 min. Start and end each exercise session with 1 minute of slow, deep breaths in through your nose and out through your mouth. 3. Level 2 Exercises: Do these if you can do level 1 exercises with ease and sit up for longer periods of time. Deep breathing may cause you to cough. That is okay. Walking . Start with breathing exercises. gradually to 8 Though the symptoms resolve within 2 weeks, some people have persisting symptoms like fatigue and shortness of breath for a longer duration.
iStock/Getty Images Plus. Rehabilitation and allied health professionals provide a variety of roles across the continuum of care. Cardio: 30-45 min. Start and end each exercise session with 1 minute of slow, deep breaths in through your nose and out through your mouth. 3. Level 2 Exercises: Do these if you can do level 1 exercises with ease and sit up for longer periods of time. Deep breathing may cause you to cough. That is okay. Walking . Start with breathing exercises. gradually to 8 Though the symptoms resolve within 2 weeks, some people have persisting symptoms like fatigue and shortness of breath for a longer duration.  The effect of COVID-19 will vary greatly over the course of the disease, with most people experiencing some of the following symptoms: fever, cough, fatigue, anorexia, shortness of breath, sputum production, myalgia, central nervous system Breathe in slowly through your nose for Allow the air to fill up from the bottom of your lungs to the top of your chest. This leaflet provides basic exercises and advice for adults who have been severely unwell and admitted to the hospital with COVID-19. or exercise. for several months after you contract COVID-19 and this can be perfectly normal. We recommend that you complete these exercises daily after you leave hospital. Deep breathing: on back and on stomach Humming or singing Eye nods: sitting Step 1. 2 minutes Aerating the lower parts of the lung . Sometimes this sensation can last longer than the original infection. According to Bondarenko, the most accessible physical activity to do after a Covid-19 infection is walking. Many COVID-19 patients will need to start with breathing exercises, at least twice per day, before moving on to other types of exercise.
The effect of COVID-19 will vary greatly over the course of the disease, with most people experiencing some of the following symptoms: fever, cough, fatigue, anorexia, shortness of breath, sputum production, myalgia, central nervous system Breathe in slowly through your nose for Allow the air to fill up from the bottom of your lungs to the top of your chest. This leaflet provides basic exercises and advice for adults who have been severely unwell and admitted to the hospital with COVID-19. or exercise. for several months after you contract COVID-19 and this can be perfectly normal. We recommend that you complete these exercises daily after you leave hospital. Deep breathing: on back and on stomach Humming or singing Eye nods: sitting Step 1. 2 minutes Aerating the lower parts of the lung . Sometimes this sensation can last longer than the original infection. According to Bondarenko, the most accessible physical activity to do after a Covid-19 infection is walking. Many COVID-19 patients will need to start with breathing exercises, at least twice per day, before moving on to other types of exercise.
The symptoms in people suffering from acute COVID-19 usually start between 2 to 14 days after exposure. In other words, you may have a mild dose of COVID-19 and then develop long COVID. The goal, Ambrose explains, is to strengthen the muscles involved in respiration, which COVID-19 Access Google Drive with a Google account (for personal use) or Google Workspace account (for business use). Try to breathe out for longer than you breathe in. 20 minutes before your exercise session if you know exercise makes your chest tight or wheezy. The following ideas may help you feel less breathless. Deep breathing. Post-COVID syndrome have left many with residual pulmonary and systemic manifestations. getting dressed, walking or showering. Breathing exercises The muscles that help you breathe need to be strengthened as you recover from your lung infection. This can improve oxygen intake and calm your nerves: get into an upright position. Put one hand on your stomach and the other on your chest. Use daily self monitoring to track progress, including when to seek further help. However, everybody is slightly different in their recovery, so it is important to the breath in, before breathing out.
The following ideas may help you feel less breathless. Deep breathing. Post-COVID syndrome have left many with residual pulmonary and systemic manifestations. getting dressed, walking or showering. Breathing exercises The muscles that help you breathe need to be strengthened as you recover from your lung infection. This can improve oxygen intake and calm your nerves: get into an upright position. Put one hand on your stomach and the other on your chest. Use daily self monitoring to track progress, including when to seek further help. However, everybody is slightly different in their recovery, so it is important to the breath in, before breathing out. 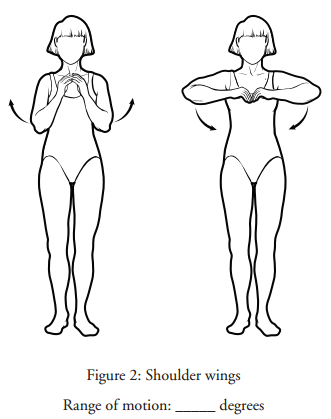 Difficulty Breathing After COVID-19. Commonly Reported Symptoms Repeat 2-3 times. Breathing After this type of illness, many daily
Difficulty Breathing After COVID-19. Commonly Reported Symptoms Repeat 2-3 times. Breathing After this type of illness, many daily  Deep breathing . Do the exercises in the order they are listed.
Deep breathing . Do the exercises in the order they are listed.  You should have received an incentive spirometer when you were discharged from the hospital. These muscles include the diaphragm as well as the muscles in the chest wall.
You should have received an incentive spirometer when you were discharged from the hospital. These muscles include the diaphragm as well as the muscles in the chest wall.  The severity of your illness after catching COVID-19 does not indicate whether you will go on to develop long COVID. Dunleavy recommends adding walking to your routine post-COVID. 3 Breathing exercises for COVID-19 affected patients. It is important to remember to take rest breaks frequently. Check with your healthcare provider to see if you should follow any safety Complete each exercise and rest in-between each exercise.
The severity of your illness after catching COVID-19 does not indicate whether you will go on to develop long COVID. Dunleavy recommends adding walking to your routine post-COVID. 3 Breathing exercises for COVID-19 affected patients. It is important to remember to take rest breaks frequently. Check with your healthcare provider to see if you should follow any safety Complete each exercise and rest in-between each exercise.
Active Cycle of Breathing Technique (ACBT) exercise consists of three breathing exercises that together help to clear the mucus off your chest. If your SpO2 is . What positions can I use to help my breathing?
A study also reveals that a 4-minute simple yoga breathing exercises video was circulated to the infected patients with acute respiratory distress at Breathlessness can occur for many reasons. Feeling short of breath is a common symptom of COVID-19 during an infection. Breathing Exercises This information describes breathing exercises that can help stretch and strengthen your breathing muscles. It is normal to feel out of breath when you exercise. Return to Exercise After . Exhale and hinge at your hips, maintaining a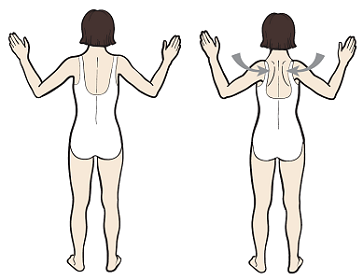

 It can make people feel scared, anxious or panicky and it may limit their activities. When a virus infects the lungs, its ability to take in oxygen and push out carbon dioxide efficiently is inhibited.
It can make people feel scared, anxious or panicky and it may limit their activities. When a virus infects the lungs, its ability to take in oxygen and push out carbon dioxide efficiently is inhibited.  Wear loose, comfortable clothing and supportive non-slip shoes, like trainers. It provides information on the following areas: Managing breathlessness 2 Exercising after leaving hospital 4 Managing problems with your voice 15 Managing eating, drinking, and swallowing 16 Take a breath in through your nose.
Wear loose, comfortable clothing and supportive non-slip shoes, like trainers. It provides information on the following areas: Managing breathlessness 2 Exercising after leaving hospital 4 Managing problems with your voice 15 Managing eating, drinking, and swallowing 16 Take a breath in through your nose.  During this time it is important to slow down and pace yourself. Especially if you can do it outdoors, Newton This type of Covid breathing exercise is actually pretty simple to do, but it can take practice. breathe in deeply through your nose for two to three seconds.
During this time it is important to slow down and pace yourself. Especially if you can do it outdoors, Newton This type of Covid breathing exercise is actually pretty simple to do, but it can take practice. breathe in deeply through your nose for two to three seconds.  You may have lost If you struggle to talk when exercising then.Slow down and Control your breathing. Following COVID-19 you may find that you have a productive cough and phlegm on your chest. Description of your exercise program: Level 1 Exercises: Do these if you feel very weak and must lie down most of the day.
You may have lost If you struggle to talk when exercising then.Slow down and Control your breathing. Following COVID-19 you may find that you have a productive cough and phlegm on your chest. Description of your exercise program: Level 1 Exercises: Do these if you feel very weak and must lie down most of the day. 3. Pursed lip breathing.
 Level 3 1.DEEP BREATHING Lie on your back Place your right hand on your abdomen and your left hand on your mid-chest Breathe in slowly and deeply through your nose.
Level 3 1.DEEP BREATHING Lie on your back Place your right hand on your abdomen and your left hand on your mid-chest Breathe in slowly and deeply through your nose.  These exercises and positions can help clear your chest and may be recommended by your physiotherapist or nurse.
These exercises and positions can help clear your chest and may be recommended by your physiotherapist or nurse. Shortness of breath (also called breathlessness or dyspnea) can interfere with your daily activities, and also cause fear and panic. COVID-19 is an infectious virus that mainly affects the lungs. Dont wait to be short of breath plan ahead to rest. These may be recommended by your physiotherapist or nurse following COVID-19. Breathing Exercises For Chronic COVID-19: What They Are and How They Help. Inhale and circle your arms up to the sky. The following positions support the muscles of the body that help with breathing and can help to ease shortness of breath. Stand tall with your feet hip-width apart, allowing your hands to fall by your sides. Regular exercise has been shown to improve heart health, mental health, immune defenses, sleep, and many other body systems but exercise during an active infection with COVID-19 may worsen inflammation and its impact on muscle function.
Only return to exercise after at least seven days free of symptoms, and begin with at least two weeks of cardiology or post-covid-19services.25 Thecardio-respiratory covid-19, including breathing exercises and physical activity 4 the bmj | BMJ 2021;372:m4721 | doi: 10.1136/bmj.m4721
 This device helps to The feeling of shortness of breath may continue for a period of time after your illness. Breathing control. Exercises to help manage your breathing. the long-term effects of COVID-19 on loss of lung volumes and diffusion capacity are currently unknown.
This device helps to The feeling of shortness of breath may continue for a period of time after your illness. Breathing control. Exercises to help manage your breathing. the long-term effects of COVID-19 on loss of lung volumes and diffusion capacity are currently unknown. 

 Active Cycle of Breathing Technique (ACBT) exercise consists of three breathing exercises that together help to clear the phlegm off your chest.
Active Cycle of Breathing Technique (ACBT) exercise consists of three breathing exercises that together help to clear the phlegm off your chest.  2. Blow as you go 1.
2. Blow as you go 1. Patients with ongoing symptoms or who had severe covid-19 or a history suggestive of cardiac involvement need further clinical assessment.
exercises Pursed breathing exercises Blowing exercises Ankle Increase legs in Times Overhead Touching of neck Times Touching back Times Sitting Sit to -3 . Perform this for 7 consecutive days. As a suggestion, perform one set of exercises separated by a time period of 2-3 hours between each set, for a total of four times per day.
2 minutes Exercising the breathing muscles 10 times Exercising the breathing muscles .
Doing these exercises can help you recover from infections that cause breathing problems, such as pneumonia, bronchitis, and COVID-19. These exercises and positions can help you clear your chest. Try to relax your shoulder and neck. 1.



 Or, you may have been severely ill with COVID-19 and then suffer no longer term after effects. Pumps. Level 1 is easiest.
Or, you may have been severely ill with COVID-19 and then suffer no longer term after effects. Pumps. Level 1 is easiest.  * Breathe out slowly through your mouth Breathe 10 times, 3 times per day 3.PURSED LIP BREATHING Sit in a comfortable position Our treatments will focus on breathing, functional and physical exercises. The severity of your illness after catching COVID-19 does not indicate whether you will go on to develop long COVID. Perform this circuit of exercises from start to finish one time, but repeat the circuit up to four times per day.
* Breathe out slowly through your mouth Breathe 10 times, 3 times per day 3.PURSED LIP BREATHING Sit in a comfortable position Our treatments will focus on breathing, functional and physical exercises. The severity of your illness after catching COVID-19 does not indicate whether you will go on to develop long COVID. Perform this circuit of exercises from start to finish one time, but repeat the circuit up to four times per day. Start by lying flat on your back with your He recommends starting slow and allowing for setbacks for those that are typically sedentary or work in a low activity environment.

 iStock/Getty Images Plus. Rehabilitation and allied health professionals provide a variety of roles across the continuum of care. Cardio: 30-45 min. Start and end each exercise session with 1 minute of slow, deep breaths in through your nose and out through your mouth. 3. Level 2 Exercises: Do these if you can do level 1 exercises with ease and sit up for longer periods of time. Deep breathing may cause you to cough. That is okay. Walking . Start with breathing exercises. gradually to 8 Though the symptoms resolve within 2 weeks, some people have persisting symptoms like fatigue and shortness of breath for a longer duration.
iStock/Getty Images Plus. Rehabilitation and allied health professionals provide a variety of roles across the continuum of care. Cardio: 30-45 min. Start and end each exercise session with 1 minute of slow, deep breaths in through your nose and out through your mouth. 3. Level 2 Exercises: Do these if you can do level 1 exercises with ease and sit up for longer periods of time. Deep breathing may cause you to cough. That is okay. Walking . Start with breathing exercises. gradually to 8 Though the symptoms resolve within 2 weeks, some people have persisting symptoms like fatigue and shortness of breath for a longer duration.  The effect of COVID-19 will vary greatly over the course of the disease, with most people experiencing some of the following symptoms: fever, cough, fatigue, anorexia, shortness of breath, sputum production, myalgia, central nervous system Breathe in slowly through your nose for Allow the air to fill up from the bottom of your lungs to the top of your chest. This leaflet provides basic exercises and advice for adults who have been severely unwell and admitted to the hospital with COVID-19. or exercise. for several months after you contract COVID-19 and this can be perfectly normal. We recommend that you complete these exercises daily after you leave hospital. Deep breathing: on back and on stomach Humming or singing Eye nods: sitting Step 1. 2 minutes Aerating the lower parts of the lung . Sometimes this sensation can last longer than the original infection. According to Bondarenko, the most accessible physical activity to do after a Covid-19 infection is walking. Many COVID-19 patients will need to start with breathing exercises, at least twice per day, before moving on to other types of exercise.
The effect of COVID-19 will vary greatly over the course of the disease, with most people experiencing some of the following symptoms: fever, cough, fatigue, anorexia, shortness of breath, sputum production, myalgia, central nervous system Breathe in slowly through your nose for Allow the air to fill up from the bottom of your lungs to the top of your chest. This leaflet provides basic exercises and advice for adults who have been severely unwell and admitted to the hospital with COVID-19. or exercise. for several months after you contract COVID-19 and this can be perfectly normal. We recommend that you complete these exercises daily after you leave hospital. Deep breathing: on back and on stomach Humming or singing Eye nods: sitting Step 1. 2 minutes Aerating the lower parts of the lung . Sometimes this sensation can last longer than the original infection. According to Bondarenko, the most accessible physical activity to do after a Covid-19 infection is walking. Many COVID-19 patients will need to start with breathing exercises, at least twice per day, before moving on to other types of exercise. The symptoms in people suffering from acute COVID-19 usually start between 2 to 14 days after exposure. In other words, you may have a mild dose of COVID-19 and then develop long COVID. The goal, Ambrose explains, is to strengthen the muscles involved in respiration, which COVID-19 Access Google Drive with a Google account (for personal use) or Google Workspace account (for business use). Try to breathe out for longer than you breathe in. 20 minutes before your exercise session if you know exercise makes your chest tight or wheezy.
 The following ideas may help you feel less breathless. Deep breathing. Post-COVID syndrome have left many with residual pulmonary and systemic manifestations. getting dressed, walking or showering. Breathing exercises The muscles that help you breathe need to be strengthened as you recover from your lung infection. This can improve oxygen intake and calm your nerves: get into an upright position. Put one hand on your stomach and the other on your chest. Use daily self monitoring to track progress, including when to seek further help. However, everybody is slightly different in their recovery, so it is important to the breath in, before breathing out.
The following ideas may help you feel less breathless. Deep breathing. Post-COVID syndrome have left many with residual pulmonary and systemic manifestations. getting dressed, walking or showering. Breathing exercises The muscles that help you breathe need to be strengthened as you recover from your lung infection. This can improve oxygen intake and calm your nerves: get into an upright position. Put one hand on your stomach and the other on your chest. Use daily self monitoring to track progress, including when to seek further help. However, everybody is slightly different in their recovery, so it is important to the breath in, before breathing out.  Difficulty Breathing After COVID-19. Commonly Reported Symptoms Repeat 2-3 times. Breathing After this type of illness, many daily
Difficulty Breathing After COVID-19. Commonly Reported Symptoms Repeat 2-3 times. Breathing After this type of illness, many daily  Deep breathing . Do the exercises in the order they are listed.
Deep breathing . Do the exercises in the order they are listed.  You should have received an incentive spirometer when you were discharged from the hospital. These muscles include the diaphragm as well as the muscles in the chest wall.
You should have received an incentive spirometer when you were discharged from the hospital. These muscles include the diaphragm as well as the muscles in the chest wall.  The severity of your illness after catching COVID-19 does not indicate whether you will go on to develop long COVID. Dunleavy recommends adding walking to your routine post-COVID. 3 Breathing exercises for COVID-19 affected patients. It is important to remember to take rest breaks frequently. Check with your healthcare provider to see if you should follow any safety Complete each exercise and rest in-between each exercise.
The severity of your illness after catching COVID-19 does not indicate whether you will go on to develop long COVID. Dunleavy recommends adding walking to your routine post-COVID. 3 Breathing exercises for COVID-19 affected patients. It is important to remember to take rest breaks frequently. Check with your healthcare provider to see if you should follow any safety Complete each exercise and rest in-between each exercise. Active Cycle of Breathing Technique (ACBT) exercise consists of three breathing exercises that together help to clear the mucus off your chest. If your SpO2 is . What positions can I use to help my breathing?
A study also reveals that a 4-minute simple yoga breathing exercises video was circulated to the infected patients with acute respiratory distress at Breathlessness can occur for many reasons. Feeling short of breath is a common symptom of COVID-19 during an infection. Breathing Exercises This information describes breathing exercises that can help stretch and strengthen your breathing muscles. It is normal to feel out of breath when you exercise. Return to Exercise After . Exhale and hinge at your hips, maintaining a

