Normal saline for secretions for Respiratory Therapy use is instilled into ET tube and 3-5 ventilated breaths performed prior to suctioning as above. Explains the purpose of a cuffed tracheostomy and when to deflate the cuff or switch to a cuffless tracheostomy tube. 

Blood stained secretions may indicate tracheal injury.
Flush the closed suction tubing with clean water and empty the water receptacle as needed. Suction pressure should not exceed -150 mmHg (-20kPa) and is appropriate for most patients. versus acute care, Demonstrate how to perform trach care (inner cannula changes, site Suctioning is alifesaving procedure requiring timely and precise methodology. The opinions expressed are those of the authors.
B MocDujeHFq@2u%I@t4an: e1wrMp:+ lra@6#R"ir. +! A tracheostomy tube bypasses the natural humidification and filtration system. Reducing suctioning times to less than 15 seconds can prevent hypoxemia. Some inner cannulas must be reinserted before connecting to the ventilator circuit. Application for continuing education credit has been made to AARC for 1 CRCE.
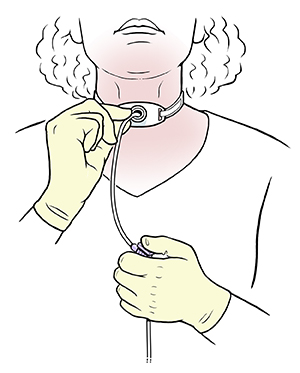
In-line suctioning preferred for indications other than obtaining material for culture. After explanation and consent, make sure to follow infection control procedures.
Removal of a fenestrated inner cannula with placement of a non-fenestrated inner cannula prevents the suction catheter from passing through the fenestrations, which can cause trauma to the tissue.
Closed suctioning consists of a catheter enclosed in an outer plastic sheathe which allows the same catheter to be used multiple times. It is difficult to discern the exact reason. /Length 10 0 R Brief, 10-second suction duration is usually recommended to avoid mucosal damage and prolonged hypoxia. : CD004581. Indications include noisy or moist respirations, prolonged expiratory breath sounds, increased respiratory effort, oxygen desaturations,restlessness, increased coughing or reduced effectiveness of coughing, increased use of accessory muscles and patient request. The visible black marker indicates that the tube is withdrawn.
9 0 obj The catheter should be introduced to the desired depth. Suctioning should be continuous, not intermittent. The Mechanical Ventilation Webinar is an hour recorded course which will help the learner to understand the role of mechanical ventilation, the settings involved with setting up mechanical ventilation and different modes of mechanical ventilation with graphs and a whiteboard for better understanding. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD004581.pub2, The Blom Tracheostomy Tube System (Pulmodyne) is a specialized tracheostomy tube which can allow adults to vocalize either with the cuff inflated or deflated. Shallow suctioning is when the suction catheter is passed to the tip of the tracheostomy tube. Course is coming soon! A catheter that is too small may not remove the secretions adequately or result in multiple attempts that can cause trauma to the airway. HtTr0wi:EXeI 3]dFle$eR 0Ma@|ui|=K`
A cuffed and non-fenestrated tracheostomy tube should be used for COVID positive patients or suspected patients. Iowa Neonatology Fellows Large quantities of blood or persistent bleeding should be investigated to determine the cause of the bleeding. Adult Tracheostomy Care: Home Edition is a 1 hour recorded webinar which provides information about performing tracheostomy care for adult patients in the home environment.
Intermittent suctioning does not reduce trauma and is less effective. [`DaaS#Fsba(#P}]7k5H[^z#6,JaX^(8m!KBM+ ,M,;W 1wJ.0#Lb},d>>`Da/iP5O'wEz d"N@y;L. The catheter may also not pass if the tube is dislodged. The tip of the suction catheter will not be inserted beyond the end of the tube. b.pq@ *R(r34Pb0'!FCVHw Suction should not be applied while the catheter is being inserted down the ET tube. The instructor will explain the relationship between compliance and resistance and provide information on different pressures related to mechanical ventilation regarding lung mechanics (PIP, pleateu pressure, transpulmonary pressures, mean airway pressures). Tracheal suctioning can be performed either with open circuit or closed circuit (Ballard) suctioning. Reattach any oxygen to the patient if indicated. Infections may result from the possible introduction of bacteria into the respiratory tract if proper suctioning techniques are not performed. Occlude the suction port with a gloved thumb and suction upon removal of the catheter.
Patients with tracheostomy are at high risk for preventable adverse events as. When withdrawing the catheter, continuous suction is applies. An individual who is awake and cooperative may be asked to cough up secretions in order to limit suctioning and potential tracheal trauma.
stream Adult Tracheostomy Care: Home Edition Webinar 20% off! Suctioning of the airways should be performed by skilled personnel with appropriatepreparation to prevent. Pre-oxygenate the patient with 100% oxygen prior to suctioning to reduce the risk of hypoxemia. fKwHWS[Lz)pb:@Zl`v . It is recommended that the external diameter of the suction catheter to be no more than half of the internal diameter of the tracheostomy tube. The inability to pass a suction catheter indicates the airway is not patent. AARC CEU- 1.0 contact hours
If done appropriately with caution, it decreases the risk of infection, pooling of secretions, and prolonged hypoxia. Please confirm you want to block this member. Tracheostomy Tubes Webinar: Comparisons and Choices is a 2 hour recorded course that is all about different types of tracheostomy tubes and how to choose the most appropriate tracheostomy tube for your patient. The tracheostomy effects the normal functions of the upper airway including secretion management and humification due to impaired cough reflex, increased mucous production and impaired actions of the cilia.
The inclusion in this publication of material relating to a particular product or method does not amount to an endorsement of its value, quality, or the claims made by its manufacturer. Suctioning with a fenestrated inner cannula may allow the catheter to pass out of the fenestration, leading to possible damage to the posterior tracheal wall. In cases of acute respiratory distress, where obstruction of the airway or the airway adjunct is suspected, suctioning must be performed emergently, with even minimal preparation.
%PDF-1.2 L@ H] RZ2 hp`9FRIpb RI0@0LC*II8D`coSFq t @9V1V The ability to forcibly cough secretions through the upper airway is one indicator for readiness of decannulation. Deflating the cuff of the tracheostomy tube has many benefits, but must be done with caution. b8r?tT
All Rights Reserved. Large quantities of blood should be investigated as to the cause of the bleeding. Risks are associated with suctioning and should be weighed with specific individual patient needs. This is a red flag and requires quick attention. If using an open suction system for a patient receiving mechanical ventilation, reattach all equipment. Complications from suctioning are relatively uncommon if performed with care and pre-oxygenation prior to suctioning. Clean hands prior to placing gloves on. Art. If the need for CPT is documented, it must be ordered by a physician describing the area to be treated and the frequency of treatments. Suctioning can be anxiety provoking for the patient. Please allow a few minutes for this process to complete. Suction between feedings or discontinue feedings for period of treatment. Ultimate responsibility for the treatment of patients and interpretation of these materials lies with the medical practitioner / user. First the inner cannula (if present) should be removed.
For effective deep suctioning, many experts advocate advancing the suction catheter until the carina, where resistance is met. eliminating the need to disconnect the individual from the ventilator. Blood stained secretions may indicate tracheal injury. Suctioning of the airways should be performed by skilled personnel with appropriatepreparation to prevent complications of suctioning.
To obtain material for analysis of culture. Removal of a fenestrated inner cannula with placement of a non-fenestrated inner cannula prevents the suction catheter from passing through the fenestrations, which can cause trauma to the tissue. It is patient dependent on the amount of secretions and their ability to clear the secretions independently. Cuffed versus cuffless tracheostomy.
Atelectasis can occur as the alveoli may close and be unavailable for gas exchange. %PDF-1.3 % 1 0 obj << /op true /OPM 1 /SM 0.02 /OP true /SA true /Type /ExtGState >> endobj 2 0 obj << /FontFile3 94 0 R /CapHeight 714 /Ascent 714 /Flags 262176 /ItalicAngle 0 /Descent -176 /XHeight 538 /FontName /HelveticaNeue-BoldCond /FontBBox [ -164 -224 1066 961 ] /StemH 138 /Type /FontDescriptor /StemV 138 >> endobj 3 0 obj << /Filter /FlateDecode /Length 720 >> stream Some individuals are able to project mucous out of the tracheostomy tube by coughing.
Suctioning should be continuous, not intermittent. University of Iowa Stead Family Childrens Hospital is part of University of Iowa Hospitals & Clinics. Cardiac dysrhythmia from the act of suctioning may disrupt the patients heart rhythm with bradycardia from stimulation of the vagal nerve. Copyright 2022 The University of Iowa. Oxygenation prior to suctioning will be done with an FiO2 no greater than 0.10 above that being used to ventilate the infant. Although tracheostomy tube changes are relatively simple and easy procedures, it should only be changed by someone who is trained and competent to do so.
Subirana M, Sol I, Benito S. Closed tracheal suction systems versus open tracheal suction systems for mechanically ventilated adult patients.
Instructor: Terrence Sheffield, RRT-ACCS, RPFT, NPS, AE-C Now available! Easy passage of a suction catheter and removal of secretions confirms proper placement and patency of the tracheostomy tube. Once an individual can tolerate a speaking valve or cap, they may be able to cough secretions around the tracheostomy tube, through the upper airway and out of the mouth. Bleeding can occur if there is trauma from the suction catheter to the tracheal wall. During the pandemic it is recommended to use a closed circuit suction to reduce opening the circuit which could result in aerosolizing.
Closed suction catheters are usually changed every 72 hours or according to manufacturer instructions. Deep suctioning may be required if shallow suctioning does not clear secretions adequately. Higher pressures may result in trauma to the tracheal tissue or hypoxia from aspirating oxygen. There are no absolute contraindications to tracheal suctioning as problems are usually short lived and related to the baseline stability of the patient.
The presence of thick viscous secretions can lead to atelectasis, a decrease in oxygenation and even collapse of the lung lobe(s).
Cough techniques can aid with secretion removal and eventual decannulation. Aa!sa52S1c1H|]/@80@UasR[pI,*;C/v)6a /wlB7,%0H9h}_N8ACSu[BPm!>Q.AA o;vJC J|`D.pOt xu and proper suctioning technique with pressures not exceeding. No. There is a delicate balance between effectively removing secretions and reducing injury to the tracheal mucosa. Webinar objectives. -#?$0)PAM gg,Cu(+ There are no absolute contraindications to suctioning. Consider a mask and goggles during the open suctioning technique, particularly if the patient has an infection or if there are copious secretions.
Anxiety can be associated with suctioning.
Do not apply suctioning while introducing the catheter as this can increase the risk of mucosal damage and hypoxemia. The entire tracheostomy tube may need to be changed if replacing the inner cannula still does not allow the suction catheter to pass. Failure to pass a suction catheter may indicate that the tube is blocked or displaced and should The Clinical Consensus Guidelines indicates that the stoma and tracheostomy tube should be suctioned when there is evidence of visual or audible secretions in the airway, suspected airway obstruction, and when the tube is changed or the cuff deflated (Mitchell, 2013). Once a need for tracheal suction has been established, the careprovider should make sure all equipment is available and functioning adequately. Vibration and percussion (CPT) will not be performed routinely prior to suctioning. resulting in less available oxygen. An apron should be worn to protect clothing and other patients. Trauma may be prevented through an appropriately sized catheter and proper suctioning technique with pressures not exceeding-150 mmHg (-20kPa).
Open suction catheters involve using singe-use catheters. The adequacy of suctioning can be assessed by the clearance of secretions, improved breath sounds, improved air entry, good pulse oximetry readings, and improvement in respiratory distress in a patient. Inability to pass the suction catheter is a red flag and indicates that the airway is not patent. Do not apply suctioning while introducing the catheter as this can increase the risk of mucosal damage and hypoxemia. Learn about active and passive humidification. Hypoxemia may result as some oxygen provided to the patient may be taken from the vacuum created during suctioning, O2 therapy wall flow meter/portable bottle and tracheostomy mask, Personal protective equipment (gloves, gown as needed, ideally goggles/mask). The Tracheostomy Tubes Webinar will provide information on patient candidacy for the types of tubes. Even those working with trach tubes for years will likely learn something new in this detail oriented course on trach tubes.
iR@WtQ'THLBpn ungyZ0wV;*) A t[SX1_,6tf|d=U0] ++z- x)0y Be!FGCEe> Easy passage of a suction catheter and removal of secretions confirms proper placement and patency of the tracheostomy tube. % An obstruction of the tracheostomy tube may be due to thick secretions or blood.
The amount of secretions varies by patient as does the amount of suctioning needs. Care shouldbe taken to maintain sterility while suctioning the endotracheal/tracheostomy tubes. Videos are used to aide in learner comprehension of tracheostomy care. /Filter /LZWDecode Airway patency can be checked by attempting suctioning at least every 8 hours. Advantages of a closed circuit suctioning are ease of use andeliminating the need to disconnect the individual from the ventilator. Tracheal damage and hypoxia can also be minimized by using an appropriately sized suction catheter.
)'R9AlM2 x;8: Learn about suctioning, inner cannulas (disposable vs non-disposable), tracheostomy tube cleaning (if indicated), stoma care, cuff management, humidification and communication with the interdisciplinary team. If the patient has a fenestrated tracheostomy tube, the unfenestrated inner cannula must be in place before suctioning. The National Tracheostomy Safety Project has an algorithm for Emergent Tracheostomy Management including cases where the suction catheter is unable to pass. Multidisciplinary tracheostomy teams have been shown to improve outcomes for patients with tracheostomy. Tracheostomy and feeding tubes are often placed concurrently. There is a delicate balance between effectively removing secretions and reducing injury to the tracheal mucosa. Find out information on timing of tracheostomy, swallowing management and communication specific for ALS. The catheter should be introduced to the desired depth. Saline may be used if the infant has thick tenacious secretions which cannot be extracted by using suctioning alone. The National Tracheostomy Safety Project has an algorithm for. Discuss patient/family education for humidification, oxygen, Education is a main role of respiratory therapist in the home environment. This technique is often used if the patient has loose secretions that are able to be coughed to the end of the tube.
j5( 6h#C9& T`|s u7 a`$',EY0QlQ"6DEy9nF)%xXa!O)H Contains spam, fake content or potential malware, Adult Tracheostomy Care Webinar: Home Edition, Tracheostomy Tubes Webinar: Comparisons and Choices, Mechanical Ventilation Webinar: Beginners Guide, Cuffed versus Cuffless Tracheostomy Tubes, Humidification and Hydration for Tracheostomy and/or Mechanical Ventilation, Identify the indications for and complications of a tracheostomy, Note the differences and limitations of tracheostomy care at home nebulizers, and mechanical ventilation with trachs.
The procedure should not take longer than 10 seconds. Speech-language pathologists may be interested in grasping ventilator information for a whole person approach. Auscultate chest prior to suctioning. When performing closed suctioning, the tip of the catheter should always be in the withdrawn position when not being used. hCL1/k91 Review the different types of speaking valves and benefits for those with tracheostomy and mechanical ventilation: Passy-Muir, Shiley, Shikani, and Montgomery. Occlude the suction port with a gloved thumb and suction upon removal of the catheter. `3TqasPAf Once resistance is met, the suction catheter should be withdrawn slightly before suctioning is commenced.
In this course, the risk of inappropriate tracheostomy tubes based on the size and length will be provided. Higher pressures may result in trauma to the tracheal tissue or hypoxia from aspirating oxygen. If the suction catheter is passed further than the end of the tracheostomy tube, this is considered deep suctioning. Suction pressure should not exceed -150 mmHg (-20kPa) and is appropriate for most patients. ?#A5e-sPL8_00L:p5@@uPV[057&[;iwM6o+rBjfT\<0|9>xT67%IR%pG A>[aA(@ @ H$I8jc\ (^sWz0(>Ul"pR.4IcC;DsH2)3Z@M%* 'P%IHeAbs{c$*ELO.!q9BC$&t9|-$&07bpfKDwJj!GcK~v ;X~O%qgE! @BNsQL$64F>j%GrJc* iPZBN&3 '+3Zgc.AA'H}eS
@D3 @ZD2//:LhlSEqytC#;#KY,l2Y*/j,${Fl
>> Support the patient in a position that will facilitate coughing (unless contraindicated). The PaO2 should be raised to a level comparable to that prior to suctioning. Hypoxemia can also result from stimulation of the vagal nerve. Tracheal suctioning is one strategy to assist in secretion management for individuals with tracheostomy. Preparation for suctioning depends on an emergentversus anon-emergent need for suctioning.