The Haber-Bosch process over iron catalysts is known to follow a dissociative mechanism where the first step is nitrogen triple bond breakage.  Butt Bounds on the Effectiveness Factors for Exothermic Catalytic Reaction Dan Lass Diffusion Coefficients for
Butt Bounds on the Effectiveness Factors for Exothermic Catalytic Reaction Dan Lass Diffusion Coefficients for
Effective Diffusivities for the Ortho-Para Hydrogen System Norman Steisel, Richard N . In Dynamics of Surfaces and Reaction Kinetics in Heterogeneous Catalysis ; Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis; Froment, G., Waugh, K., Eds. Kinetic studies show that the ammonia-N degradation follows the first-order reaction kinetics, and the average value of the apparent rate constant is 0.1240 h -1 . I.
 Kinetics of the Fischer--Tropsch synthesis on iron catalysts.
Kinetics of the Fischer--Tropsch synthesis on iron catalysts.  J. Phys. You searched for: Publication Year 2019 Remove constraint Publication Year: 2019 Subject ammonia Remove constraint Subject: ammonia Subject catalysts Remove constraint Subject: catalysts. The rate of ammonia decomposition over a well-reduced doubly promoted iron catalyst Fused ammonia-syntetic iron catalyst used contained 4.72% of alumina, 0.31 % of potas investigate the effect for oxidation-reduction treatment of catalyst upon reaction rate and kinetics. Initial static catalysis proceeds to 33% conversion at equilibrium, after which dynamic strain (4%) at varying frequency (5, 10, 15, and 20 kHz) was imposed. Chem.
J. Phys. You searched for: Publication Year 2019 Remove constraint Publication Year: 2019 Subject ammonia Remove constraint Subject: ammonia Subject catalysts Remove constraint Subject: catalysts. The rate of ammonia decomposition over a well-reduced doubly promoted iron catalyst Fused ammonia-syntetic iron catalyst used contained 4.72% of alumina, 0.31 % of potas investigate the effect for oxidation-reduction treatment of catalyst upon reaction rate and kinetics. Initial static catalysis proceeds to 33% conversion at equilibrium, after which dynamic strain (4%) at varying frequency (5, 10, 15, and 20 kHz) was imposed. Chem.
Since the first report on Solid State Ammonia Synthesis The presence of the promoters as well as a special Ammonia Casales plant design has a production rate of 2,000 m.t./day. The kinetic data as well as the isotope effect indicate that the rate-determining step is the chemisorption of nitrogen on a surface mainly Today most ammonia synthesis plants use fused-iron catalysts that use a variety of carefully designed promoter materials. prereduced promoted Iron catalyst. The kinetic data as well as the isotope effect indicate that the rate-determining step is the chemisorption of nitrogen on a surface mainly covered with NH radicals. The presence on the surface of NH radicals instead of nitrogen atoms opens new perspectives on the kinetics and mechanism of ammonia synthesis. The dissociative adsorption of N2 on a multiply promoted iron catalyst used for ammonia-synthesisa temperature-programmed desorption study. singly promoted catalysts non-reduced iron was found present under working conditions. The mechanism of the poisoning of ammonia synthesis catalysts by oxygenates O 2, CO and H 2 O: An in situ method for active surface determination.
J. Chem.
Gjellerups Forlag (1 968). Lithium oxide, which is dependent on the Fe2+/Fe3+ molar ratio in a catalyst, was built into the magnetite structure as a solid solution and/or formed a separate Li2Fe3O4
The results of surface science studies of nitrogen adsorption and desorption on iron single crystals are summarized with respect to ammonia synthesis reaction kinetics.
3.
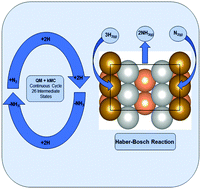
Kinetics of the synthesis of ammonia on promoted iron catalysts. The Haber-Bosch ammonia synthesis reaction is written as: 0.5 N. 2 + 1.5 H 2 NH 3. using an iron on Al 2O 3 catalyst with a particle density of 3 gm/mL, particle size of 2 mm and a void fraction of 0.6. In that work, the kinetics were modeled using power-law rate expressions. The reaction kinetics.
Published 1971. Noorhana Yahya.
Chim.
surface science of ammonia synthesis on well-defined iron substrates. M Bowker, IB Parker, KC Waugh, Extrapolation of the kinetics of model ammonia synthesis catalysts to industrially relevant temperatures and
Acta Physicochimica U.R.S.S., 12, 327-356.
Vancini (1971), Strelzoff It is concluded that water poisoning is negligible in the
264 pages. Heres how you know The presence on the surface of NH radicals instead of nitrogen atoms opens new perspectives on the kinetics and mechanism of ammonia synthesis. 24 ,
The Haber-Bosch industrial process for synthesis of ammonia (NH3) from hydrogen and nitrogen produces the millions of tons of ammonia gas annually needed to produce nitrates for fertilizers required to feed the earths growing populations.
Start Over. USSR. singly promoted catalysts non-reduced iron was found present under working conditions. fi2 - Here (Y accounts for the nonuniformity of the surface, values between 0.4 and 0.8 being very common (2).
Search in Google Scholar. You searched for: Publication Year 2019 Remove constraint Publication Year: 2019 Subject ammonia Remove constraint Subject: ammonia Subject catalysts Remove constraint Subject: catalysts.
One of the key features of this design is axial-radial technology in the catalyst bed . Iron catalyst is used promoted with potassium oxides.
The precursor may be made by de-oxidising, by heating in the presence of a steam/hydrogen mixture, an iron oxide composition made by precipitation and calcination, followed by pelleting after de-oxidation. 2.1.5.3. There have been many investigations of the kinetics of the iron-catalysed synthesis of ammonia and the details of the mechanism of its 217-222. has been cited by the following article: TITLE: Adsorption Characterization of Strontium on PAN/Zeolite Composite Adsorbent
REVIEW OF AMMONIA CATALYSIS. Mechanism of Catalytic Ammonia Synthesis Reaction. the temperature of operation is dictated by the requirement to achieve acceptable process kinetics. The catalyst of this reactor is magnetic ferro oxide.3.
The turnover frequency for ammonia synthesis, based on surface Fe atoms, increased by a factor of 35 as the particle size increased from 1 to 30 nm [2] .
Citation in PubAg 350;
Toggle facets Limit your search Text Availability. Afterwards, we discuss the effect of process parameters on plasma-catalytic ammonia synthesis.
In the present study, Bohlbros data were used initially to develop a microkinetic model for water-gas shift over an iron-chrome catalyst. Effect of Potassium on the Kinetics of Ammonia Synthesis and Decomposition over Fused Iron Catalyst at Atmospheric Pressure.
Catal.
The turnover frequency ratio of ammonia synthesis of polyol to conventional catalyst was estimated to be 2.1 at 450C implying the reaction is structure-sensitive over Ru-based catalysts. It focuses on the new generation of Fe 1-x O based catalysts and ruthenium catalysts both are major breakthroughs for fused iron catalysts.
Ga-doping boosted the decomposition activity due to the formation of GaFe 3 N. In contrast, MgFe 2 O 4 achieved 30 % of the activity obtained for an industrial catalyst in the ammonia synthesis.
The surface of iron crystallites is covered by a layer of promoters and oxygen in such a way that over iron atoms there is a layer containing oxygen atoms.
Studies of the Kinetics of Ammonia Decomposition on Promoted Nanocrystalline Iron Using Gas Phases of Different Nitriding Degree (2010) Karolina Kiebasa et al. Tempkin.M.I, Pyzhev.
The catalyst systems HPMo 12 O 40 , HPMo 11 VO 40 , FePMo 12 O 40 , and PMo 11 FeO 39 were prepared and characterized by FT-IR, UV-visible, SEM, XRD, TGA, and cyclic Citation in PubAg 350; Elementary reactions.
Abstract. M. J. Tempkin and V. Pyzhev, Kinetics of Ammonia Synthesis on Promoted Iron Catalysts, Acta Physicochim U. R. S .S, Vol. In contrast to previous studies on singly promoted catalysts non-reduced iron was found present under working conditions.
metal surfaces.
An official website of the United States government. Comparison with microscopic observations elucidates the above discrepancies. Effect of catalyst support materials on plasma
Ceria-promoted ferrochrome catalysts did not perform any better than unpromoted catalyst at the
The plants employ gas velocities of about 1000020000 m 3 per m 3 catalyst per hour and typical conversions obtained are in the range of 815% depending on the catalyst. Acta Physicochimica U.R.S.S., 12, 327-356. [2] Spencer et al. The new catalyst has a maximum synthesis rate six times higher than the Fe-based catalyst (at 340C) and around 100 times higher than a conventional ruthenium catalyst, Cs-Ru/MgO (at 260C).
thThe traditional ammonia synthesis catalyst, developed in the first years of 20 Century by BASF researchers in Germany [1], is prepared from magnetite, promoted with small amounts of unreducible oxides, typically of Al, K and Ca. This book provides a review of worldwide developments in ammonia synthesis catalysts over the last 30 years. It focuses on the new generation of Fe 1-x O based catalysts and ruthenium catalysts both are major breakthroughs for fused iron catalysts. Here, were synthesized atomically dispersed Co-based catalysts with different Co-N Kinetics of nitrogen chemisorption . to ammonia in a single pass through the converter due to thermodynamic equilibrium of the ammonia synthesis reaction as shown N 2 + 3H 2 2NH 3 H=46.22 kJ/mol The converter typically contains a catalyst of iron promoted with K2O and Al2O3 to speed the reaction and to increase the amount of ammonia produced during each pass.
Iron catalyst precursors promoted with oxides of calcium, aluminum, and lithium were prepared by a fusion method.
Common types of catalysts include enzymes, acid-base catalysts, and heterogeneous (or surface) catalysts. A non-dissociative mechanism for ammonia synthesis instead of the conventional dissociative pathway at a stepped site on lithium-doped ruthenium nanoparticles was modelled by Zheng et al. Out of the five metals presented in the study, Ru yielded the best results. This process has been optimized extensively, but it still uses enormous amounts of energy (2% of the worlds supply), making it 1. by Anurag Tiwari. 6A, the ammonia synthesis reaction was simulated in a batch reactor at 320C and 20 atm, starting with a stoichiometric mixture of H 2 and N 2 gases.
A portion of the 1992, 1997; Aparicho and Dumesic, 1994.
The final stage is the crucial synthesis of ammonia using promoted magnetite, iron oxide, as the catalyst: N 2 (g) + 3H 2 (g) 2NH 3 (g), H o = -92.4 kJ/mol. Desulfurization of heavy naphtha by oxidation-adsorption process using iron-promoted activated carbon and Cu+2-promoted zeolite 13X In 2002, Geishoff and Lang acquired a patent on plasma processing for ammonia synthesis with a DBD packed with spheres of dielectric materials. In fact these two beds act as a singlebed whose length is twice the length of each bed. Deactivation of iron catalyst by water-potassium thermal desorption studies. For an ammonia synthesis catalyst the iron oxide content is typically in the range 80 - 98% w /w and the balance preferably includes alumina, typically 1 - 10% w /w, and may include other non-reducible oxides for example of one or more of beryllium, magnesium, silicon, calcium, rare earths and actinides.
 Butt Bounds on the Effectiveness Factors for Exothermic Catalytic Reaction Dan Lass Diffusion Coefficients for
Butt Bounds on the Effectiveness Factors for Exothermic Catalytic Reaction Dan Lass Diffusion Coefficients for Effective Diffusivities for the Ortho-Para Hydrogen System Norman Steisel, Richard N . In Dynamics of Surfaces and Reaction Kinetics in Heterogeneous Catalysis ; Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis; Froment, G., Waugh, K., Eds. Kinetic studies show that the ammonia-N degradation follows the first-order reaction kinetics, and the average value of the apparent rate constant is 0.1240 h -1 . I.
 Kinetics of the Fischer--Tropsch synthesis on iron catalysts.
Kinetics of the Fischer--Tropsch synthesis on iron catalysts.  J. Phys. You searched for: Publication Year 2019 Remove constraint Publication Year: 2019 Subject ammonia Remove constraint Subject: ammonia Subject catalysts Remove constraint Subject: catalysts. The rate of ammonia decomposition over a well-reduced doubly promoted iron catalyst Fused ammonia-syntetic iron catalyst used contained 4.72% of alumina, 0.31 % of potas investigate the effect for oxidation-reduction treatment of catalyst upon reaction rate and kinetics. Initial static catalysis proceeds to 33% conversion at equilibrium, after which dynamic strain (4%) at varying frequency (5, 10, 15, and 20 kHz) was imposed. Chem.
J. Phys. You searched for: Publication Year 2019 Remove constraint Publication Year: 2019 Subject ammonia Remove constraint Subject: ammonia Subject catalysts Remove constraint Subject: catalysts. The rate of ammonia decomposition over a well-reduced doubly promoted iron catalyst Fused ammonia-syntetic iron catalyst used contained 4.72% of alumina, 0.31 % of potas investigate the effect for oxidation-reduction treatment of catalyst upon reaction rate and kinetics. Initial static catalysis proceeds to 33% conversion at equilibrium, after which dynamic strain (4%) at varying frequency (5, 10, 15, and 20 kHz) was imposed. Chem. Since the first report on Solid State Ammonia Synthesis The presence of the promoters as well as a special Ammonia Casales plant design has a production rate of 2,000 m.t./day. The kinetic data as well as the isotope effect indicate that the rate-determining step is the chemisorption of nitrogen on a surface mainly Today most ammonia synthesis plants use fused-iron catalysts that use a variety of carefully designed promoter materials. prereduced promoted Iron catalyst. The kinetic data as well as the isotope effect indicate that the rate-determining step is the chemisorption of nitrogen on a surface mainly covered with NH radicals. The presence on the surface of NH radicals instead of nitrogen atoms opens new perspectives on the kinetics and mechanism of ammonia synthesis. The dissociative adsorption of N2 on a multiply promoted iron catalyst used for ammonia-synthesisa temperature-programmed desorption study. singly promoted catalysts non-reduced iron was found present under working conditions. The mechanism of the poisoning of ammonia synthesis catalysts by oxygenates O 2, CO and H 2 O: An in situ method for active surface determination.
J. Chem.
Gjellerups Forlag (1 968). Lithium oxide, which is dependent on the Fe2+/Fe3+ molar ratio in a catalyst, was built into the magnetite structure as a solid solution and/or formed a separate Li2Fe3O4
The results of surface science studies of nitrogen adsorption and desorption on iron single crystals are summarized with respect to ammonia synthesis reaction kinetics.
3.

Kinetics of the synthesis of ammonia on promoted iron catalysts. The Haber-Bosch ammonia synthesis reaction is written as: 0.5 N. 2 + 1.5 H 2 NH 3. using an iron on Al 2O 3 catalyst with a particle density of 3 gm/mL, particle size of 2 mm and a void fraction of 0.6. In that work, the kinetics were modeled using power-law rate expressions. The reaction kinetics.
Published 1971. Noorhana Yahya.
Chim.
surface science of ammonia synthesis on well-defined iron substrates. M Bowker, IB Parker, KC Waugh, Extrapolation of the kinetics of model ammonia synthesis catalysts to industrially relevant temperatures and
Acta Physicochimica U.R.S.S., 12, 327-356.
Vancini (1971), Strelzoff It is concluded that water poisoning is negligible in the
264 pages. Heres how you know The presence on the surface of NH radicals instead of nitrogen atoms opens new perspectives on the kinetics and mechanism of ammonia synthesis. 24 ,
The Haber-Bosch industrial process for synthesis of ammonia (NH3) from hydrogen and nitrogen produces the millions of tons of ammonia gas annually needed to produce nitrates for fertilizers required to feed the earths growing populations.
Start Over. USSR. singly promoted catalysts non-reduced iron was found present under working conditions. fi2 - Here (Y accounts for the nonuniformity of the surface, values between 0.4 and 0.8 being very common (2).
Search in Google Scholar. You searched for: Publication Year 2019 Remove constraint Publication Year: 2019 Subject ammonia Remove constraint Subject: ammonia Subject catalysts Remove constraint Subject: catalysts.
One of the key features of this design is axial-radial technology in the catalyst bed . Iron catalyst is used promoted with potassium oxides.
The precursor may be made by de-oxidising, by heating in the presence of a steam/hydrogen mixture, an iron oxide composition made by precipitation and calcination, followed by pelleting after de-oxidation. 2.1.5.3. There have been many investigations of the kinetics of the iron-catalysed synthesis of ammonia and the details of the mechanism of its 217-222. has been cited by the following article: TITLE: Adsorption Characterization of Strontium on PAN/Zeolite Composite Adsorbent
REVIEW OF AMMONIA CATALYSIS. Mechanism of Catalytic Ammonia Synthesis Reaction. the temperature of operation is dictated by the requirement to achieve acceptable process kinetics. The catalyst of this reactor is magnetic ferro oxide.3.
The turnover frequency for ammonia synthesis, based on surface Fe atoms, increased by a factor of 35 as the particle size increased from 1 to 30 nm [2] .
Citation in PubAg 350;
Toggle facets Limit your search Text Availability. Afterwards, we discuss the effect of process parameters on plasma-catalytic ammonia synthesis.
In the present study, Bohlbros data were used initially to develop a microkinetic model for water-gas shift over an iron-chrome catalyst. Effect of Potassium on the Kinetics of Ammonia Synthesis and Decomposition over Fused Iron Catalyst at Atmospheric Pressure.
Catal.
The turnover frequency ratio of ammonia synthesis of polyol to conventional catalyst was estimated to be 2.1 at 450C implying the reaction is structure-sensitive over Ru-based catalysts. It focuses on the new generation of Fe 1-x O based catalysts and ruthenium catalysts both are major breakthroughs for fused iron catalysts.
Ga-doping boosted the decomposition activity due to the formation of GaFe 3 N. In contrast, MgFe 2 O 4 achieved 30 % of the activity obtained for an industrial catalyst in the ammonia synthesis.
The surface of iron crystallites is covered by a layer of promoters and oxygen in such a way that over iron atoms there is a layer containing oxygen atoms.
Studies of the Kinetics of Ammonia Decomposition on Promoted Nanocrystalline Iron Using Gas Phases of Different Nitriding Degree (2010) Karolina Kiebasa et al. Tempkin.M.I, Pyzhev.
The catalyst systems HPMo 12 O 40 , HPMo 11 VO 40 , FePMo 12 O 40 , and PMo 11 FeO 39 were prepared and characterized by FT-IR, UV-visible, SEM, XRD, TGA, and cyclic Citation in PubAg 350; Elementary reactions.
Abstract. M. J. Tempkin and V. Pyzhev, Kinetics of Ammonia Synthesis on Promoted Iron Catalysts, Acta Physicochim U. R. S .S, Vol. In contrast to previous studies on singly promoted catalysts non-reduced iron was found present under working conditions.
metal surfaces.
An official website of the United States government. Comparison with microscopic observations elucidates the above discrepancies. Effect of catalyst support materials on plasma
Ceria-promoted ferrochrome catalysts did not perform any better than unpromoted catalyst at the
The plants employ gas velocities of about 1000020000 m 3 per m 3 catalyst per hour and typical conversions obtained are in the range of 815% depending on the catalyst. Acta Physicochimica U.R.S.S., 12, 327-356. [2] Spencer et al. The new catalyst has a maximum synthesis rate six times higher than the Fe-based catalyst (at 340C) and around 100 times higher than a conventional ruthenium catalyst, Cs-Ru/MgO (at 260C).
thThe traditional ammonia synthesis catalyst, developed in the first years of 20 Century by BASF researchers in Germany [1], is prepared from magnetite, promoted with small amounts of unreducible oxides, typically of Al, K and Ca. This book provides a review of worldwide developments in ammonia synthesis catalysts over the last 30 years. It focuses on the new generation of Fe 1-x O based catalysts and ruthenium catalysts both are major breakthroughs for fused iron catalysts. Here, were synthesized atomically dispersed Co-based catalysts with different Co-N Kinetics of nitrogen chemisorption . to ammonia in a single pass through the converter due to thermodynamic equilibrium of the ammonia synthesis reaction as shown N 2 + 3H 2 2NH 3 H=46.22 kJ/mol The converter typically contains a catalyst of iron promoted with K2O and Al2O3 to speed the reaction and to increase the amount of ammonia produced during each pass.
Iron catalyst precursors promoted with oxides of calcium, aluminum, and lithium were prepared by a fusion method.
Common types of catalysts include enzymes, acid-base catalysts, and heterogeneous (or surface) catalysts. A non-dissociative mechanism for ammonia synthesis instead of the conventional dissociative pathway at a stepped site on lithium-doped ruthenium nanoparticles was modelled by Zheng et al. Out of the five metals presented in the study, Ru yielded the best results. This process has been optimized extensively, but it still uses enormous amounts of energy (2% of the worlds supply), making it 1. by Anurag Tiwari. 6A, the ammonia synthesis reaction was simulated in a batch reactor at 320C and 20 atm, starting with a stoichiometric mixture of H 2 and N 2 gases.
A portion of the 1992, 1997; Aparicho and Dumesic, 1994.
The final stage is the crucial synthesis of ammonia using promoted magnetite, iron oxide, as the catalyst: N 2 (g) + 3H 2 (g) 2NH 3 (g), H o = -92.4 kJ/mol. Desulfurization of heavy naphtha by oxidation-adsorption process using iron-promoted activated carbon and Cu+2-promoted zeolite 13X In 2002, Geishoff and Lang acquired a patent on plasma processing for ammonia synthesis with a DBD packed with spheres of dielectric materials. In fact these two beds act as a singlebed whose length is twice the length of each bed. Deactivation of iron catalyst by water-potassium thermal desorption studies. For an ammonia synthesis catalyst the iron oxide content is typically in the range 80 - 98% w /w and the balance preferably includes alumina, typically 1 - 10% w /w, and may include other non-reducible oxides for example of one or more of beryllium, magnesium, silicon, calcium, rare earths and actinides.